LiDAR technology (Light Detection and Ranging) has become an essential tool in various fields, from land mapping to autonomous driving. But what is LiDAR, how does it work, and what are its practical applications?
In this article, we will explore how LiDAR works, its main uses, advantages, and limitations.
What is LiDAR?
LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances with extreme precision. The system emits thousands of laser pulses per second toward a surface and measures the time it takes for each pulse to reflect back to the sensor.
Using these measurements, LiDAR calculates the distance between the sensor and objects, creating a three-dimensional (3D) map of the environment in real time.
LiDAR is particularly valuable in situations where centimeter-level accuracy is crucial. Unlike methods such as photogrammetry, which rely on images, LiDAR can “see” through vegetation or transparent structures, measuring terrain and objects even in low-light conditions or dense forests.
LiDAR in Action: A Practical Example
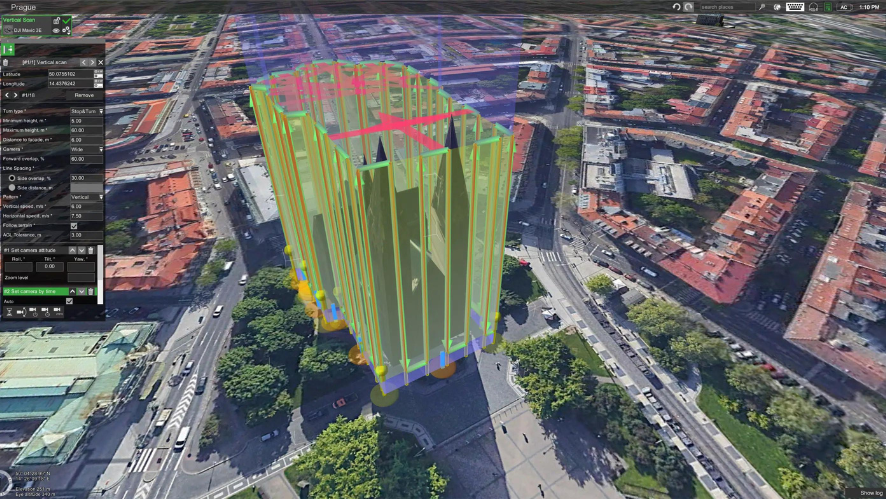
Imagine we need to map a forest to analyze its density. With a drone equipped with LiDAR technology, we can fly over the area and, thanks to the laser pulses penetrating the vegetation, create a map that shows not only the tree canopies but also the ground, revealing the terrain’s relief and variations in vegetation density.
Main Applications of LiDAR
- Mapping and Topographic Surveys: LiDAR is widely used in topography to create detailed maps of terrain, making it indispensable for construction projects, urban planning, and environmental engineering.
- Autonomous Driving: In the automotive industry, LiDAR enables autonomous vehicles to “see” their surroundings, identifying obstacles, vehicles, and pedestrians with high accuracy.
- Archaeology: LiDAR has proven invaluable for archaeologists, allowing them to identify ancient ruins hidden beneath dense vegetation, where conventional techniques often struggle to deliver results.
- Precision Agriculture: In agriculture, LiDAR is used to analyze the structure of soil and vegetation, enabling the monitoring of crop health and optimizing irrigation systems.
- Forest Management and Conservation: For forests, LiDAR provides detailed information on tree height, density, and structure, helping monitor biodiversity and prevent wildfires.
Advantages of LiDAR Technology
- High precision: LiDAR’s ability to measure with centimeter-level accuracy makes it superior to traditional methods in many applications.
- Real-time data collection: It allows for the instantaneous creation of detailed 3D maps.
- Operation in complex environments: It works effectively in densely wooded or vegetated areas where other methods, such as photographic imagery, are less effective.
Examples of Drones with LiDAR Technology
The market for drones equipped with LiDAR technology has grown rapidly, with models designed for applications ranging from terrain mapping to infrastructure inspection.
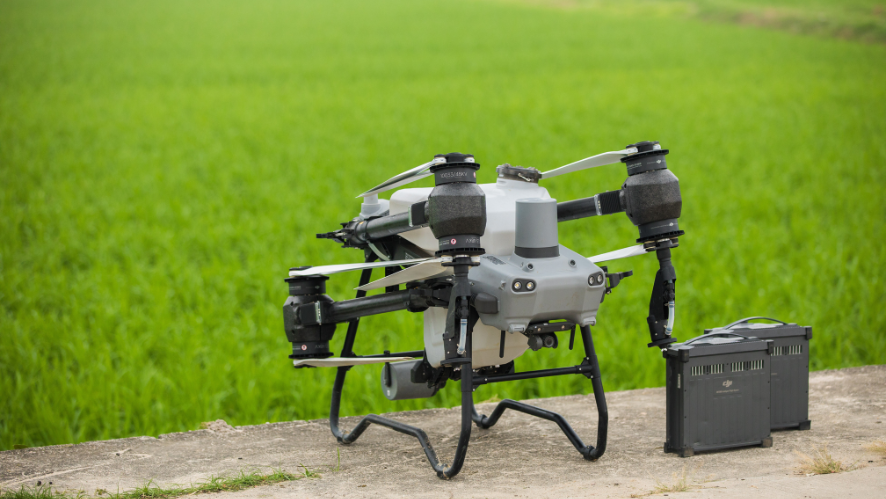
- DJI Matrice 350 RTK with Zenmuse L2: The DJI Matrice 350 RTK is one of the most popular drones for professional applications. Equipped with the DJI Zenmuse L2 sensor (LiDAR), this model offers high-precision 3D mapping, making it ideal for topography and forest management.
- Yellowscan Mapper: Yellowscan is a brand specializing in LiDAR solutions, and its Mapper model can be adapted to various drones, including the DJI Matrice. This system is especially useful for land surveys and natural disaster monitoring due to its precision and ease of integration with drones from different manufacturers.
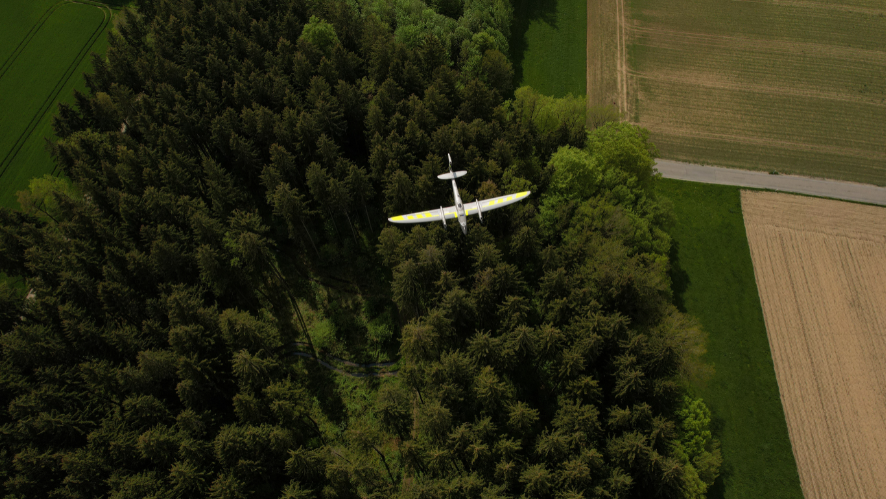
- Quantum Systems Trinity Pro: This VTOL drone (vertical takeoff and landing) is compatible with LiDAR sensors and is known for its efficiency in mapping large areas, such as forests or agricultural fields. Its long-range flight capability and LiDAR precision make it a popular choice for mapping projects in extensive and remote areas.
Conclusion
LiDAR technology is an impressive advancement that is transforming how we understand and interact with the environment. With applications ranging from autonomous driving to forest conservation, LiDAR is a powerful tool for solving complex challenges and expanding our knowledge of the world.