What is LiDAR?
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances between the sensor and objects on the ground. Based on these measurements, it is possible to generate extremely accurate three-dimensional models of terrain, vegetation, structures, and buildings.
LiDAR vs. traditional photogrammetry
While traditional photogrammetry uses overlapping images to reconstruct topography through triangulation, LiDAR directly measures distances, generating high-density point clouds, even in areas with dense vegetation or topographical variations.
| Criterion | LiDAR | Traditional photogrammetry |
| Altimeter accuracy | High (±2 cm) | Average (±5-10 cm) |
| Efficiency in vegetation | Excellent | Limited |
| Processing time | Faster | Slower |
Practical applications in drones
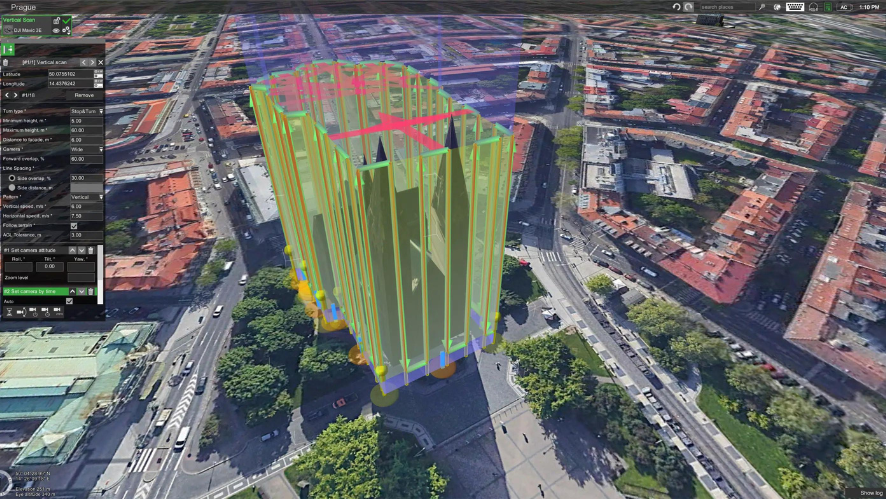
The integration of LiDAR sensors into long-range drones such as the DJI Matrice 350 RTK + Zenmuse L2 has enabled high-precision topographic surveys to be carried out in record time, especially in:
- Civil engineering and construction projects (digital terrain modeling)
- Forest monitoring and forest inventory
- Public infrastructure management (roads, dams, tunnels)
How does LiDAR work on drones?
The combination of LiDAR sensors with professional drones, such as the DJI Matrice 400 or the DJI Matrice 350 RTK + Zenmuse L2, is completely changing the paradigm of photogrammetry and surveying. Main advantages:
✅ 1. Mapping with high altimetric precision
Unlike image-based photogrammetry, LiDAR directly measures distances, enabling superior vertical accuracy (±2-3 cm), even on uneven terrain or in dense vegetation.
✅ 2. Data collection in areas with dense vegetation
LiDAR lasers are capable of penetrating vegetation and reaching the ground, allowing topographic models to be generated even in forests, jungles, or agricultural areas with dense vegetation cover, something that is impossible with conventional photogrammetry.
✅ 3. Operational efficiency and rapid coverage
A drone equipped with a LiDAR sensor can map hundreds of hectares per day without the need for ground control points (GCPs), saving hours of fieldwork and reducing post-processing time.
✅ 4. Safety and accessibility
LiDAR drones prevent technicians from accessing dangerous or difficult-to-reach areas (slopes, cliffs, active construction sites), reducing operational risks.
_________________________________________________________________________